Vocabulary at Girlington
‘The development of children’s spoken language underpins all seven areas of learning and development. Children’s back-and-forth interactions from an early age form the foundations for language and cognitive development. The number and quality of the conversations they have with adults and peers throughout the day in a language-rich environment is crucial. By commenting on what children are interested in or doing, and echoing back what they say with new vocabulary added, practitioners will build children’s language effectively. Reading frequently to children, and engaging them actively in stories, non-fiction, rhymes and poems, and then providing them with extensive opportunities to use and embed new words in a range of contexts, will give children the opportunity to thrive. Through conversation, story-telling and role play, where children share their ideas with support and modelling from their teacher, and sensitive questioning that invites them to elaborate, children become comfortable using a rich range of vocabulary and language structures’ Statutory framework for the early years foundation stage 2021
‘Pupils’ acquisition and command of vocabulary are key to their learning and progress across the whole curriculum. Teachers should therefore develop vocabulary actively, building systematically on pupils’ current knowledge.’ National Curriculum 2014.
Aims
At Girlington, our aim is to provide children with a rich and varied vocabulary where words are fully embedded, so that children are able to apply them to their own spoken language, independent reading and writing.
Guidelines
Teachers select words to teach specifically using the focus text of the topic. These words are selected based on children’s prior knowledge, words they need to know to access the text and the use of the ‘Three Tier Model of Vocabulary’.
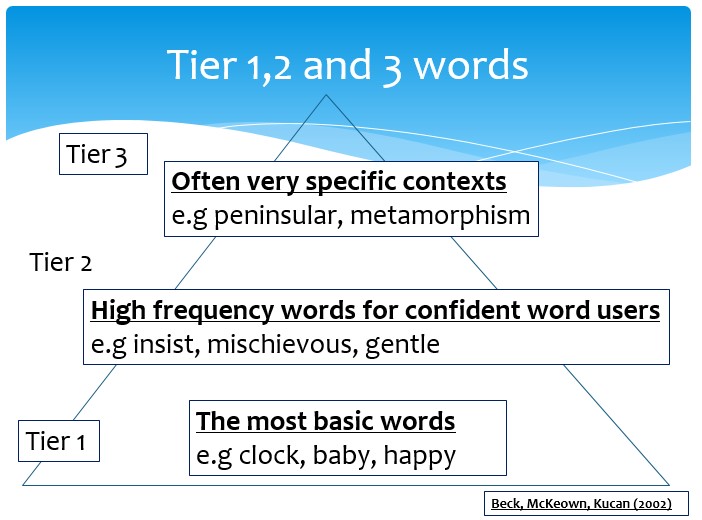
Across the curriculum we actively plan opportunities for teaching the children a productive vocabulary. To teach vocabulary we often use the stepped approach:
- Contextualise the word.
- Repeat the word.
- Explain the meaning.
- Provide other examples.
- Relate to own experiences.
- Engage with the words in other ways.
- Record word in a sentence


The Speech Language and Communication curriculum maps cover acquisition and progression of vocabulary.
